Amphenicol
In this article, we will explore the impact and implications of Amphenicol on modern society. From its emergence to its influence on different aspects of daily life, Amphenicol has played a crucial role in shaping various fields, such as politics, economics, technology and culture. Through in-depth analysis, we will examine how Amphenicol has evolved over time and how it has shaped the perceptions and actions of people around the world. Additionally, we will address the controversies and debates that Amphenicol has generated, as well as its potential impact in the future. This article seeks to provide a comprehensive and insightful view on Amphenicol and its importance in contemporary society.
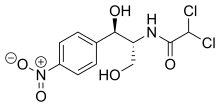

Amphenicols are a class of antibiotics with a phenylpropanoid structure. They function by blocking the enzyme peptidyl transferase on the 50S ribosome subunit of bacteria.
Examples of amphenicols include chloramphenicol, thiamphenicol, azidamfenicol, and florfenicol. The first-in-class compound was chloramphenicol, introduced in 1949. Chloramphenicol was initially discovered as a natural product and isolated from the soil bacteria Steptomyces venezuelae; however, all amphenicols are now made by chemical synthesis.
References
- ^ "APVMA: Florfenicol". Archived from the original on 2007-09-07. Retrieved 2007-07-22.
- ^ Scholar, Eric (2007). "Chloramphenicol". X Pharm: The Comprehensive Pharmacology Reference. pp. 1–7. doi:10.1016/B978-008055232-3.61439-4. ISBN 9780080552323.
- ^ Berendsen, Bjorn; Stolker, Linda; De Jong, Jacob; Nielen, Michel; Tserendorj, Enkhtuya; Sodnomdarjaa, Ruuragchas; Cannavan, Andrew; Elliott, Christopher (2010). "Evidence of natural occurrence of the banned antibiotic chloramphenicol in herbs and grass". Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 397 (5): 1955–1963. doi:10.1007/s00216-010-3724-6. PMC 2886120. PMID 20431869.