Labyrinthine artery
In this article, we will explore the exciting world of Labyrinthine artery and everything that this theme has to offer. From its origins to its impact today, we will immerse ourselves in a journey of discovery to fully understand the importance and relevance of Labyrinthine artery in our lives. Through an exhaustive analysis, we will examine the different facets and aspects that make Labyrinthine artery a topic of universal interest, addressing everything from its social impact to its global implications. With interviews with experts, statistical data and diverse perspectives, this article aims to be a complete guide that unravels the mysteries and virtues of Labyrinthine artery, offering a comprehensive vision that allows the reader to delve into the fascinating universe of this topic.
| Labyrinthine artery | |
|---|---|
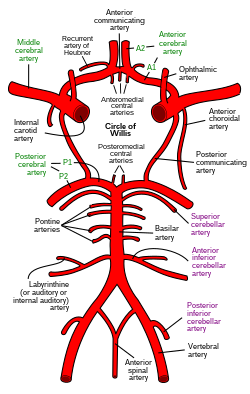 Diagram of the arterial circulation at the base of the brain. (Internal auditory artery labeled at center left.) | |
| Details | |
| Source | Anterior inferior cerebellar artery or basilar artery |
| Vein | Internal auditory veins |
| Supplies | Inner ear |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria labyrinthi, arteria auditiva interna |
| TA98 | A12.2.08.020 |
| TA2 | 4551 |
| FMA | 50548 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The labyrinthine artery (auditory artery, internal auditory artery) is a branch of either the anterior inferior cerebellar artery or the basilar artery. It accompanies the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) through the internal acoustic meatus. It supplies blood to the internal ear.
Structure
The labyrinthine artery is a branch of either the anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) or the basilar artery.[1][2] It accompanies the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) through the internal acoustic meatus.[1] It divides into a cochlear branch and a labyrinthine (or anterior vestibular) branch.[1]
Function
The labyrinthine artery supplies blood to the inner ear.[1][3] It also supplies the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) along its length.[3]
Clinical significance
The labyrinthine artery may become occluded.[3] This can cause loss of hearing and balance on the affected side.[3]
History
The labyrinthine artery may also be known as the internal auditory artery or the auditory artery.
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 580 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 580 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ a b c d Moini, Jahangir; Piran, Pirouz (2020). "12 - Auditory system". Functional and Clinical Neuroanatomy - A Guide for Health Care Professionals. Academic Press. pp. 363–392. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-817424-1.00012-4. ISBN 978-0-12-817424-1. S2CID 242466369.
- ^ Wilkinson, J. L. (1992). "14 - Blood supply of the central nervous system". Neuroanatomy for Medical Students (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. pp. 253–264. doi:10.1016/B978-0-7506-1447-4.50018-9. ISBN 978-0-7506-1447-4.
- ^ a b c d Walker, M. (2014). "Vestibular System". Encyclopedia of the Neurological Sciences - Reference Module in Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Psychology (2nd ed.). Academic Press. pp. 647–656. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-385157-4.01185-4. ISBN 978-0-12-385158-1.
External links
- "Anatomy diagram: 13048.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2014-01-01.
