Corticopontine fibers
In today's world, Corticopontine fibers has become a topic of great relevance and interest to a wide variety of people. From professionals to enthusiasts, Corticopontine fibers has captured the attention of many due to its many facets and its impact on different aspects of everyday life. Whether on a personal, professional or social level, Corticopontine fibers has proven to be a topic worthy of analysis and reflection. In this article, we will thoroughly explore the various dimensions of Corticopontine fibers and its relevance in today's world. From its history to its future implications, we will dive into an exhaustive analysis that seeks to shed light on this fascinating topic.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (November 2008) |
| Corticopontine fibers | |
|---|---|
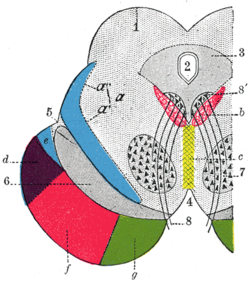 Coronal section through mid-brain. 1. Corpora quadrigemina. 2. Cerebral aqueduct. 3. Central gray stratum. 4. Interpeduncular space. 5. Sulcus lateralis. 6. Substantia nigra. 7. Red nucleus of tegmentum. 8. Oculomotor nerve, with 8’, its nucleus of origin. a. Lemniscus (in blue) with a’ the medial lemniscus and a" the lateral lemniscus. b. Medial longitudinal fasciculus. c. Raphé. d. Temporopontine fibers. e. Portion of medial lemniscus, which runs to the lentiform nucleus and insula. f. Cerebrospinal fibers. g. Frontopontine fibers. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | fibrae corticopontinae, tractus corticopontinus |
| NeuroNames | 1322 |
| TA98 | A14.1.05.107 |
| TA2 | 5619 |
| FMA | 75190 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
Corticopontine fibers are projections from the cerebral cortex to the pontine nuclei.
Depending upon the lobe of origin, they can be classified as frontopontine fibers, parietopontine fibers, temporopontine fibers or occipitopontine fibers.
References
- ^ Kamali A, Kramer LA, Frye RE, Butler IJ, Hasan KM (October 2010). "Diffusion tensor tractography of the human brain cortico-ponto-cerebellar pathways: a quantitative preliminary study". J Magn Reson Imaging. 32 (4): 809–17. doi:10.1002/jmri.22330. PMC 4492525. PMID 20882611.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Leergaard TB, Bjaalie JG (November 2007). "Topography of the complete corticopontine projection: From experiments to principal Maps". Front Neurosci. 1 (1): 211–23. doi:10.3389/neuro.01.1.1.016.2007. PMC 2518056. PMID 18982130.
- ^ http://braininfo.rprc.washington.edu/AncilDefinition.aspx?ID=1322&questID=1322[permanent dead link]
External links
Cortex->Pons->Cerebellum: