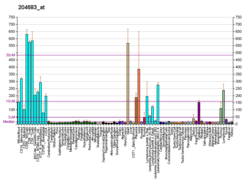
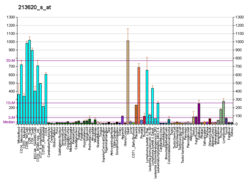
ICAM2
In this article, we are going to delve deeper into the topic of ICAM2, exploring its many facets and providing a holistic view that allows the reader to better understand its importance and relevance in different contexts. From its impact on modern society to its influence on the personal level, ICAM2 is a topic that continues to arouse interest and generate debate. Through in-depth analysis and a wide range of examples, we will examine the various dimensions of ICAM2, addressing its global implications and highlighting its role in shaping our current environment. Whether you are an expert in the field or simply curious to learn more, this article promises to offer a rich and insightful perspective on ICAM2.
| ICAM2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | ICAM2, CD102, intercellular adhesion molecule 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 146630; MGI: 96394; HomoloGene: 675; GeneCards: ICAM2; OMA:ICAM2 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Intercellular adhesion molecule 2 (ICAM2), also known as CD102 (Cluster of Differentiation 102), is a human gene, and the protein resulting from it.
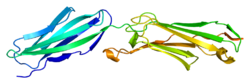
Protein structure
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM) family. All ICAM proteins are type I transmembrane glycoproteins, contain 2–9 immunoglobulin-like C2-type domains, and bind to the leukocyte adhesion LFA-1 protein.
Protein functions
ICAM-2 molecules regulate spermatid adhesion on Sertoli cell on the apical side of the blood-testis barrier (towards the lumen), thus playing a major role in spermatogenesis.[5]
This protein may also play a role in lymphocyte recirculation by blocking LFA-1-dependent cell adhesion. It mediates adhesive interactions important for antigen-specific immune response, NK-cell mediated clearance, lymphocyte recirculation, and other cellular interactions important for immune response and surveillance.[6]
Interactions
ICAM2 has been shown to interact with EZR.[7] It has also been shown to bind to P9 (Uniprot: B2UM07), a secreted protein from Akkermansia muciniphila.[8]
See also
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000108622 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000001029 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Xiao X, Mruk DD, Cheng CY (2013). "Intercellular adhesion molecules (ICAMs) and spermatogenesis". Human Reproduction Update. 19 (2): 167–86. doi:10.1093/humupd/dms049. PMC 3576004. PMID 23287428.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: ICAM2 intercellular adhesion molecule 2".
- ^ Heiska L, Alfthan K, Grönholm M, Vilja P, Vaheri A, Carpén O (August 1998). "Association of ezrin with intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and -2 (ICAM-1 and ICAM-2). Regulation by phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-bisphosphate". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 273 (34): 21893–900. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.34.21893. PMID 9705328.
- ^ Yoon HS, Cho CH, Yun MS, Jang SJ, You HJ, Kim JH, Han D, Cha KH, Moon SH, Lee K, Kim YJ, Lee SJ, Nam TW, Ko G (May 2021). "Akkermansia muciniphila secretes a glucagon-like peptide-1-inducing protein that improves glucose homeostasis and ameliorates metabolic disease in mice". Nature Microbiology. 6 (5): 563–573. doi:10.1038/s41564-021-00880-5. PMID 33820962. S2CID 233037565.
Further reading
- Simmons DL (1995). "The role of ICAM expression in immunity and disease". Cancer Surveys. 24: 141–55. PMID 7553659.
- Hayflick JS, Kilgannon P, Gallatin WM (1998). "The intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM) family of proteins. New members and novel functions". Immunologic Research. 17 (3): 313–27. doi:10.1007/BF02786454. PMID 9638475. S2CID 19901365.
- Lalor PF, Shields P, Grant A, Adams DH (February 2002). "Recruitment of lymphocytes to the human liver". Immunology and Cell Biology. 80 (1): 52–64. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1711.2002.01062.x. PMID 11869363. S2CID 19892941.
- Yonekawa K, Harlan JM (February 2005). "Targeting leukocyte integrins in human diseases". Journal of Leukocyte Biology. 77 (2): 129–40. doi:10.1189/jlb.0804460. PMID 15548573. S2CID 44606865.
- de Fougerolles AR, Stacker SA, Schwarting R, Springer TA (July 1991). "Characterization of ICAM-2 and evidence for a third counter-receptor for LFA-1". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 174 (1): 253–67. doi:10.1084/jem.174.1.253. PMC 2118873. PMID 1676048.
- Sansom D, Borrow J, Solomon E, Trowsdale J (October 1991). "The human ICAM2 gene maps to 17q23-25". Genomics. 11 (2): 462–4. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(91)90157-A. PMID 1769660.
- Staunton DE, Dustin ML, Springer TA (May 1989). "Functional cloning of ICAM-2, a cell adhesion ligand for LFA-1 homologous to ICAM-1". Nature. 339 (6219): 61–4. Bibcode:1989Natur.339...61S. doi:10.1038/339061a0. PMID 2497351. S2CID 4326657.
- Bujía J, Holly A, Kim C, Scanady N, Kastenbauer E (1994). "Expression of human intercellular adhesion molecules in middle ear cholesteatoma". American Journal of Otolaryngology. 15 (4): 271–5. doi:10.1016/0196-0709(94)90094-9. PMID 7526720.
- de Fougerolles AR, Qin X, Springer TA (February 1994). "Characterization of the function of intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-3 and comparison with ICAM-1 and ICAM-2 in immune responses". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 179 (2): 619–29. doi:10.1084/jem.179.2.619. PMC 2191386. PMID 7905020.
- Butini L, De Fougerolles AR, Vaccarezza M, Graziosi C, Cohen DI, Montroni M, Springer TA, Pantaleo G, Fauci AS (September 1994). "Intercellular adhesion molecules (ICAM)-1 ICAM-2 and ICAM-3 function as counter-receptors for lymphocyte function-associated molecule 1 in human immunodeficiency virus-mediated syncytia formation". European Journal of Immunology. 24 (9): 2191–5. doi:10.1002/eji.1830240939. PMID 7916296. S2CID 24872330.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (January 1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Hirao M, Sato N, Kondo T, Yonemura S, Monden M, Sasaki T, Takai Y, Tsukita S, Tsukita S (October 1996). "Regulation mechanism of ERM (ezrin/radixin/moesin) protein/plasma membrane association: possible involvement of phosphatidylinositol turnover and Rho-dependent signaling pathway". The Journal of Cell Biology. 135 (1): 37–51. doi:10.1083/jcb.135.1.37. PMC 2121020. PMID 8858161.
- Bernstein CN, Sargent M, Gallatin WM, Wilkins J (October 1996). "Beta 2-integrin/intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM) expression in the normal human intestine". Clinical and Experimental Immunology. 106 (1): 160–9. PMID 8870715.
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (September 1996). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery". Genome Research. 6 (9): 791–806. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791. PMID 8889548.
- Casasnovas JM, Springer TA, Liu JH, Harrison SC, Wang JH (May 1997). "Crystal structure of ICAM-2 reveals a distinctive integrin recognition surface". Nature. 387 (6630): 312–5. Bibcode:1997Natur.387..312C. doi:10.1038/387312a0. PMID 9153399. S2CID 4276760.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, Suyama A, Sugano S (October 1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Sainio M, Zhao F, Heiska L, Turunen O, den Bakker M, Zwarthoff E, Lutchman M, Rouleau GA, Jääskeläinen J, Vaheri A, Carpén O (September 1997). "Neurofibromatosis 2 tumor suppressor protein colocalizes with ezrin and CD44 and associates with actin-containing cytoskeleton". Journal of Cell Science. 110. 110 (18): 2249–60. doi:10.1242/jcs.110.18.2249. PMID 9378774.
- Yonemura S, Hirao M, Doi Y, Takahashi N, Kondo T, Tsukita S, Tsukita S (February 1998). "Ezrin/radixin/moesin (ERM) proteins bind to a positively charged amino acid cluster in the juxta-membrane cytoplasmic domain of CD44, CD43, and ICAM-2". The Journal of Cell Biology. 140 (4): 885–95. doi:10.1083/jcb.140.4.885. PMC 2141743. PMID 9472040.
- Bernstein CN, Sargent M, Gallatin WM (February 1998). "Beta2 integrin/ICAM expression in Crohn's disease". Clinical Immunology and Immunopathology. 86 (2): 147–60. doi:10.1006/clin.1997.4462. PMID 9473377.
External links
- ICAM2+protein,+human at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- PDBe-KB provides an overview of all the structure information available in the PDB for Human Intercellular adhesion molecule 2 (ICAM2)
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.