Portal:World
In this article, we will take a closer look at the impact Portal:World has had on our society. From its emergence to the present, Portal:World has played a crucial role in various areas of our daily lives. Over the years, Portal:World has played a fundamental role in the way we communicate, work and interact with our environment. This article seeks to offer a deep and insightful view on the importance of Portal:World, as well as its influence on the contemporary world. Through an exhaustive analysis, we will explore the many facets of Portal:World and its impact on different spheres of society, providing the reader with a broad and enriching perspective on this topic.
Portal maintenance status: (No date set)
|
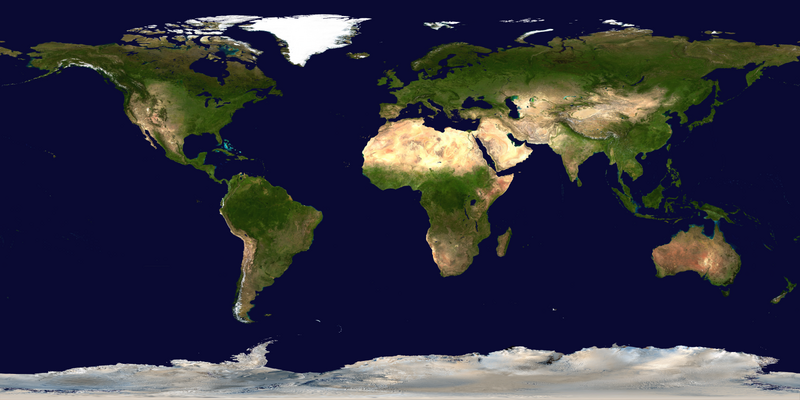
The World Portal

The world is the totality of entities, the whole of reality, or everything that exists. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object while others analyze the world as a complex made up of parts.
In scientific cosmology, the world or universe is commonly defined as "he totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". Theories of modality talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. Phenomenology, starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon or the "horizon of all horizons". In philosophy of mind, the world is contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind. Theology conceptualizes the world in relation to God, for example, as God's creation, as identical to God or as the two being interdependent. In religions, there is a tendency to downgrade the material or sensory world in favor of a spiritual world to be sought through religious practice. A comprehensive representation of the world and our place in it, as is found in religions, is known as a worldview. Cosmogony is the field that studies the origin or creation of the world while eschatology refers to the science or doctrine of the last things or of the end of the world.
In various contexts, the term "world" takes a more restricted meaning associated, for example, with the Earth and all life on it, with humanity as a whole or with an international or intercontinental scope. In this sense, world history refers to the history of humanity as a whole and world politics is the discipline of political science studying issues that transcend nations and continents. Other examples include terms such as "world religion", "world language", "world government", "world war", "world population", "world economy", or "world championship". (Full article...)
Selected articles - show another
-
Image 1

Global average temperatures show that the Medieval Warm Period was not a planet-wide phenomenon, and that the Little Ice Age was not a distinct planet-wide time period but rather the end of a long temperature decline that preceded recent global warming.
The temperature record of the last 2,000 years is reconstructed using data from climate proxy records in conjunction with the modern instrumental temperature record which only covers the last 170 years at a global scale. Large-scale reconstructions covering part or all of the 1st millennium and 2nd millennium have shown that recent temperatures are exceptional: the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Fourth Assessment Report of 2007 concluded that "Average Northern Hemisphere temperatures during the second half of the 20th century were very likely higher than during any other 50-year period in the last 500 years and likely the highest in at least the past 1,300 years." The curve shown in graphs of these reconstructions is widely known as the hockey stick graph because of the sharp increase in temperatures during the last century. this broad pattern was supported by more than two dozen reconstructions, using various statistical methods and combinations of proxy records, with variations in how flat the pre-20th-century "shaft" appears. Sparseness of proxy records results in considerable uncertainty for earlier periods.
Individual proxy records, such as tree ring widths and densities used in dendroclimatology, are calibrated against the instrumental record for the period of overlap. Networks of such records are used to reconstruct past temperatures for regions: tree ring proxies have been used to reconstruct Northern Hemisphere extratropical temperatures (within the tropics trees do not form rings) but are confined to land areas and are scarce in the Southern Hemisphere which is largely ocean. Wider coverage is provided by multiproxy reconstructions, incorporating proxies such as lake sediments, ice cores and corals which are found in different regions, and using statistical methods to relate these sparser proxies to the greater numbers of tree ring records. The "Composite Plus Scaling" (CPS) method is widely used for large-scale multiproxy reconstructions of hemispheric or global average temperatures; this is complemented by Climate Field Reconstruction (CFR) methods which show how climate patterns have developed over large spatial areas, making the reconstruction useful for investigating natural variability and long-term oscillations as well as for comparisons with patterns produced by climate models. (Full article...) -
Image 2World map showing real GDP growth rates for 2009; countries in brown were in a recession.
The Great Recession was a period of marked general decline observed in national economies globally, i.e. a recession, that occurred in the late 2000s. The scale and timing of the recession varied from country to country (see map). At the time, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) concluded that it was the most severe economic and financial meltdown since the Great Depression. One result was a serious disruption of normal international relations.
The causes of the Great Recession include a combination of vulnerabilities that developed in the financial system, along with a series of triggering events that began with the bursting of the United States housing bubble in 2005–2012. When housing prices fell and homeowners began to abandon their mortgages, the value of mortgage-backed securities held by investment banks declined in 2007–2008, causing several to collapse or be bailed out in September 2008. This 2007–2008 phase was called the subprime mortgage crisis. The combination of banks unable to provide funds to businesses, and homeowners paying down debt rather than borrowing and spending, resulted in the Great Recession that began in the U.S. officially in December 2007 and lasted until June 2009, thus extending over 19 months. As with most other recessions, it appears that no known formal theoretical or empirical model was able to accurately predict the advance of this recession, except for minor signals in the sudden rise of forecast probabilities, which were still well under 50%. (Full article...) -
Image 3Hotspots of sulfate aerosol pollution in 2005–2007 are highlighted in orange. Such sulfates rarely occur naturally outside of volcanic activity, and their increased levels are the main cause of global dimming
Global dimming is a decline in the amount of sunlight reaching the Earth's surface. It is caused by atmospheric particulate matter, predominantly sulfate aerosols, which are components of air pollution. Global dimming was observed soon after the first systematic measurements of solar irradiance began in the 1950s. This weakening of visible sunlight proceeded at the rate of 4–5% per decade until the 1980s. During these years, air pollution increased due to post-war industrialization. Solar activity did not vary more than the usual during this period.
As aerosols have a cooling effect, global dimming has masked the extent of global warming experienced to date, with the most-polluted regions even experiencing cooling in the 1970s. Global dimming has interfered with the water cycle by lowering evaporation, and thus has probably reduced rainfall in certain areas. It may have weakened the Monsoon of South Asia and caused the entire tropical rain belt to shift southwards between 1950 and 1985, with a limited recovery afterwards. Record levels of particulate pollution in the Northern Hemisphere caused or at least exacerbated the monsoon failure behind the 1984 Ethiopian famine. (Full article...) -
Image 4

Lac Gentau in the Ossau Valley of the Pyrenees, France
A lake is a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from the ocean, although they may be connected with the ocean by rivers, such as Lake Ontario. Most lakes are freshwater and account for almost all the world's surface freshwater, but some are salt lakes with salinities even higher than that of seawater. Lakes vary significantly in surface area and volume.
Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which are also water-filled basins on land, although there are no official definitions or scientific criteria distinguishing the two. Lakes are also distinct from lagoons, which are shallow tidal pools dammed by sandbars at coastal regions of oceans or large lakes. Most lakes are fed by springs, and both fed and drained by creeks and rivers, but some lakes are endorheic without any outflow, while volcanic lakes are filled directly by precipitation runoffs and do not have any inflow streams. (Full article...) -
Image 5The Kyoto Protocol (Japanese: 京都議定書, Hepburn: Kyōto Giteisho) was an international treaty which extended the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) that commits state parties to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, based on the scientific consensus that global warming is occurring and that human-made CO2 emissions are driving it. The Kyoto Protocol was adopted in Kyoto, Japan, on 11 December 1997 and entered into force on 16 February 2005. There were 192 parties (Canada withdrew from the protocol, effective December 2012) to the Protocol in 2020.
The Kyoto Protocol implemented the objective of the UNFCCC to reduce the onset of global warming by reducing greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere to "a level that would prevent dangerous anthropogenic interference with the climate system" (Article 2). The Kyoto Protocol applied to the seven greenhouse gases listed in Annex A: carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), nitrogen trifluoride (NF3). Nitrogen trifluoride was added for the second compliance period during the Doha Round. (Full article...) -
Image 6

Hands holding a tree inside of a light bulb
Action for Climate Empowerment (ACE) is a term adopted by the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). It refers to Article 6 of the Convention's original text (1992), focusing on six priority areas: education, training, public awareness, public participation, public access to information, and international cooperation on these issues. The implementation of all six areas has been identified as the pivotal factor for everyone to understand and participate in solving the complex challenges presented by climate change. The importance of ACE is reflected in other international frameworks such as the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs, 2015); the Global Action Programme for Education for Sustainable Development (GAP on ESD, 2014); the Aarhus Convention (2011); the Escazú Agreement (2018) and the Bali Guidelines (2010).
ACE calls on governments to develop and implement educational and public awareness programmes, train scientific, technical and managerial personnel, foster access to information, and promote public participation in addressing climate change and its effects. It also urges countries to cooperate in this process, by exchanging good practices and lessons learned, and strengthening national institutions. This wide scope of activities is guided by specific objectives that, together, are seen as crucial for effectively implementing climate adaptation and mitigation actions, and for achieving the ultimate objective of the UNFCCC. (Full article...) -
Image 7
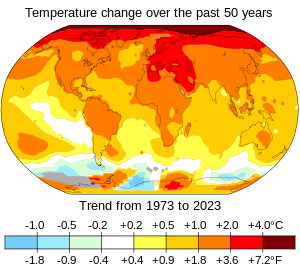
Changes in surface air temperature over the past 50 years. The Arctic has warmed the most, and temperatures on land have generally increased more than sea surface temperatures.
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global average temperature is more rapid than previous changes, and is primarily caused by humans burning fossil fuels. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices add to greenhouse gases, notably carbon dioxide and methane. Greenhouse gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight. Larger amounts of these gases trap more heat in Earth's lower atmosphere, causing global warming.
Climate change has an increasingly large impact on the environment. Deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Amplified warming in the Arctic has contributed to thawing permafrost, retreat of glaciers and sea ice decline. Higher temperatures are also causing more intense storms, droughts, and other weather extremes. Rapid environmental change in mountains, coral reefs, and the Arctic is forcing many species to relocate or become extinct. Even if efforts to minimise future warming are successful, some effects will continue for centuries. These include ocean heating, ocean acidification and sea level rise. (Full article...)
General images - load new batch
-
Image 4A Benin Bronze head from Nigeria
-
Image 6Artist's impression of a Hadean landscape with the relatively newly formed Moon still looming closely over Earth and both bodies sustaining strong volcanism. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 7"Lucy", the first Australopithecus afarensis skeleton found. Lucy was only 1.06 m (3 ft 6 in) tall.
-
Image 8Chloroplasts in the cells of a moss (from History of Earth)
-
Image 9Artist's conception of Hadean Eon Earth, when it was much hotter and inhospitable to all forms of life. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 10First airplane, the Wright Flyer, flew on 17 December 1903.
-
Image 11Obelisk of Axum, Ethiopia
-
Image 12A reconstruction of human history based on fossil data. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 16Last Moon landing: Apollo 17 (1972)
-
Image 17The replicator in virtually all known life is deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA is far more complex than the original replicator and its replication systems are highly elaborate. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 18Trilobites first appeared during the Cambrian period and were among the most widespread and diverse groups of Paleozoic organisms. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 20Notre-Dame de Paris, France
-
Image 21Great Pyramids of Giza, Egypt
-
Image 22Artist's impression of Earth during the later Archean, the largely cooled planetary crust and water-rich barren surface, marked by volcanoes and continents, features already round microbialites. The Moon, still orbiting Earth much closer than today and still dominating Earth's sky, produced strong tides. (from History of Earth)
-
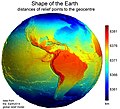
Image 24Earth's western hemisphere showing topography relative to Earth's center instead of to mean sea level, as in common topographic maps (from Earth)
-
Image 26Geologic map of North America, color-coded by age. From most recent to oldest, age is indicated by yellow, green, blue, and red. The reds and pinks indicate rock from the Archean.
-
Image 27Ajloun Castle, Jordan
-
Image 28A map of heat flow from Earth's interior to the surface of Earth's crust, mostly along the oceanic ridges (from Earth)
-
Image 29Yggdrasil, an attempt to reconstruct the Norse world tree which connects the heavens, the world, and the underworld. (from World)
-
Image 30Tiktaalik, a fish with limb-like fins and a predecessor of tetrapods. Reconstruction from fossils about 375 million years old. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 31A 580 million year old fossil of Spriggina floundensi, an animal from the Ediacaran period. Such life forms could have been ancestors to the many new forms that originated in the Cambrian Explosion. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 33A High Desert storm, sweeps across the Mojave (from Earth)
-
Image 34Dinosaurs were the dominant terrestrial vertebrates throughout most of the Mesozoic (from History of Earth)
-
Image 35A schematic view of Earth's magnetosphere with solar wind flowing from left to right (from Earth)
-
Image 36Map of peopling of the world (Southern Dispersal paradigm), in thousands of years ago.
-
Image 37Battle during 1281 Mongol invasion of Japan
-
Image 38Angkor Wat temple complex, Cambodia, early 12th century
-
Image 39Artist's impression of the enormous collision that probably formed the Moon (from History of Earth)
-
Image 42A banded iron formation from the 3.15 Ga Moodies Group, Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa. Red layers represent the times when oxygen was available; gray layers were formed in anoxic circumstances. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 47Graph showing range of estimated partial pressure of atmospheric oxygen through geologic time (from History of Earth)
-
Image 48Earth's night-side upper atmosphere appearing from the bottom as bands of afterglow illuminating the troposphere in orange with silhouettes of clouds, and the stratosphere in white and blue. Next the mesosphere (pink area) extends to the orange and faintly green line of the lowest airglow, at about one hundred kilometers at the edge of space and the lower edge of the thermosphere (invisible). Continuing with green and red bands of aurorae streching over several hundred kilometers. (from Earth)
-
Image 49An artist's impression of the Archean, the eon after Earth's formation, featuring round stromatolites, which are early oxygen-producing forms of life from billions of years ago. After the Late Heavy Bombardment, Earth's crust had cooled, its water-rich barren surface is marked by continents and volcanoes, with the Moon still orbiting Earth half as far as it is today, appearing 2.8 times larger and producing strong tides. (from Earth)
-
Image 50Vitruvian Man by Leonardo da Vinci epitomizes the advances in art and science seen during the Renaissance. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 51Earth's axial tilt causing different angles of seasonal illumination at different orbital positions around the Sun (from Earth)
-
Image 52An animation of the changing density of productive vegetation on land (low in brown; heavy in dark green) and phytoplankton at the ocean surface (low in purple; high in yellow) (from Earth)
-
Image 53Pale orange dot, an artist's impression of Early Earth, featuring its tinted orange methane-rich early atmosphere (from Earth)
-
Image 54A 2012 artistic impression of the early Solar System's protoplanetary disk from which Earth and other Solar System bodies were formed (from Earth)
-
Image 56Change in average surface air temperature and drivers for that change. Human activity has caused increased temperatures, with natural forces adding some variability. (from Earth)
-
Image 58A view of Earth with different layers of its atmosphere visible: the troposphere with its clouds casting shadows, a band of stratospheric blue sky at the horizon, and a line of green airglow of the lower thermosphere around an altitude of 100 km, at the edge of space (from Earth)
-
Image 59Tracy Caldwell Dyson, a NASA astronaut, observing Earth from the Cupola module at the International Space Station on 11 September 2010 (from Earth)
-
Image 62Fall of the Berlin Wall, 1989
-
Image 63Shanghai. China urbanized rapidly in the 21st century.
-
Image 64Great Mosque of Kairouan, Tunisia, founded 670 CE
-
Image 66A view of Earth with its global ocean and cloud cover, which dominate Earth's surface and hydrosphere; at Earth's polar regions, its hydrosphere forms larger areas of ice cover. (from Earth)
-
Image 67A pillar at Göbekli Tepe
-
Image 68Artist's rendition of an oxinated fully-frozen Snowball Earth with no remaining liquid surface water. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 69Japanese depiction of a Portuguese carrack. European maritime innovations led to proto-globalization.
-
Image 71Empires of the world in 1898
-
Image 72Astronaut Buzz Aldrin on the Moon, photographed by Neil Armstrong, 1969 (from History of Earth)
-
Image 73Pangaea was a supercontinent that existed from about 300 to 180 Ma. The outlines of the modern continents and other landmasses are indicated on this map. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 74A composite image of Earth, with its different types of surface discernible: Earth's surface dominating Ocean (blue), Africa with lush (green) to dry (brown) land and Earth's polar ice in the form of Antarctic sea ice (grey) covering the Antarctic or Southern Ocean and the Antarctic ice sheet (white) covering Antarctica. (from Earth)
-
Image 77A computer-generated image mapping the prevalence of artificial satellites and space debris around Earth in geosynchronous and low Earth orbit (from Earth)
-
Image 78Standing Buddha from Gandhara, 2nd century CE
-
Image 80The pale orange dot, an artist's impression of the early Earth which might have appeared orange through its hazy methane rich prebiotic second atmosphere. Earth's atmosphere at this stage was somewhat comparable to today's atmosphere of Titan. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 82Lithified stromatolites on the shores of Lake Thetis, Western Australia. Archean stromatolites are the first direct fossil traces of life on Earth. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 83The Pantheon, originally a Roman temple, now a Catholic church
-
Image 84Atomic bombing of Nagasaki, 1945
-
Image 86An artist's impression of ice age Earth at glacial maximum. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 88Earth's land use for human agriculture (from Earth)
-
Image 91A reconstruction of Pannotia (550 Ma). (from History of Earth)
-
Image 92Olmec colossal head, now at the Museo de Antropología de Xalapa
Megacities of the world - show another
Manila (/məˈnɪlə/ mə-NIL-ə; Filipino: Maynila, pronounced [majˈnilaʔ]), officially the City of Manila (Filipino: Lungsod ng Maynila, [luŋˈsod nɐŋ majˈnilaʔ]), is the capital and second-most-populous city of the Philippines. Located on the eastern shore of Manila Bay on the island of Luzon, it is classified as a highly urbanized city. As of 2019, it is the world's most densely populated city proper. It was the first chartered city in the country, and was designated as such by the Philippine Commission Act No. 183 on July 31, 1901. It became autonomous with the passage of Republic Act No. 409, "The Revised Charter of the City of Manila", on June 18, 1949. Manila is considered to be part of the world's original set of global cities because its commercial networks were the first to extend across the Pacific Ocean and connect Asia with the Spanish Americas through the galleon trade; when this was accomplished, it was the first time an uninterrupted chain of trade routes circling the planet had been established.
By 1258, a Tagalog-fortified polity called Maynila existed on the site of modern Manila. On June 24, 1571, after the defeat of the polity's last indigenous Rajah Sulayman in the Battle of Bangkusay, Spanish conquistador Miguel López de Legazpi began constructing the walled fortification Intramuros on the ruins of an older settlement from whose name the Spanish-and-English name Manila derives. Manila was used as the capital of the captaincy general of the Spanish East Indies, which included the Marianas, Guam and other islands, and was controlled and administered for the Spanish crown by Mexico City in the Viceroyalty of New Spain. (Full article...)Did you know - load new batch

- ... that photographing Elliot Page for the cover of Time "really meant the world" to Canadian photographer Wynne Neilly?
- ... that after bombing in World War II, the surviving tower of the Friedenskirche, a Lutheran church in Stuttgart, was combined with a new concrete structure?
- ... that VMB-611 was the only United States Marine Corps bombing squadron to operate in the Philippines during World War II?
- ... that the Baratal limestone in Russia may be one of the oldest atolls in the world?
- ... that Larry Herndon hit a game-winning home run in the 1984 World Series and a playoff-clinching home run on the last day of the 1987 season?
- ... that the play-by-mail game Westworld was run from prison?
- ... that John Spencer won a World Snooker Championship on his first attempt in 1969?
- ... that Raymond Bushland and Edward F. Knipling won the 1992 World Food Prize for developing the sterile insect technique which eliminated parasitic screw-worms from the United States?
Countries of the world - show another

Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, Finland to the east, and is connected to Denmark in the southwest by a bridge–tunnel across the Öresund.
At 450,295 square kilometres (173,860 sq mi), Sweden is the largest Nordic country and the fifth-largest country in Europe. The capital and largest city is Stockholm. Sweden has a population of 10.5 million, and a low population density of 25.5 inhabitants per square kilometre (66/sq mi), with around 87% of Swedes residing in urban areas, which cover 1.5% of the entire land area, in the central and southern half of the country. Nature in Sweden is dominated by forests and many lakes, including some of the largest in Europe. Many long rivers run from the Scandes range, primarily emptying into the northern tributaries of the Baltic Sea. It has an extensive coastline and most of the population lives near a major body of water. With the country ranging from 55°N to 69°N, the climate of Sweden is diverse due to the length of the country. (Full article...)
The Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, also known as the Seven Wonders of the World or simply the Seven Wonders, is a list of seven notable structures present during classical antiquity. The first known list of seven wonders dates back to the 2nd–1st century BC.
While the entries have varied over the centuries, the seven traditional wonders are the Great Pyramid of Giza, the Colossus of Rhodes, the Lighthouse of Alexandria, the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus, the Temple of Artemis, the Statue of Zeus at Olympia, and the Hanging Gardens of Babylon. Using modern-day countries, two of the wonders were located in Greece, two in Turkey, two in Egypt, and one in Iraq. Of the seven wonders, only the Pyramid of Giza, which is also by far the oldest of the wonders, still remains standing, while the others have been destroyed over the centuries. There is scholarly debate over the exact nature of the Hanging Gardens, and there is doubt as to whether they existed at all. (Full article...)Related portals
Protected areas of the world - load new batch
-
Image 1The Ulyanovsk Oblast in Russia contains about 118 protected natural areas. (Full article...)
-
Image 2This is a list of protected areas of Sierra Leone, including national parks, game reserves, conservation areas, wetlands, and those that are listed as proposed protected areas in the UN Environment Programme World Conservation Monitoring Centre (UNEP WCM) database. (Full article...)
-
Image 3Forests in the state of Himachal Pradesh (northern India) currently cover an area of nearly 37,939 square kilometres (14,648 sq mi), which is about 68.16% of the total land area of the state. The forests were once considered to be the main source of income of the state and most of the original forests were clear felled. The emphasis has shifted, however, from exploitation to conservation. The state government aims to increase forest cover to 50% of the total land area. There have been various projects, including the establishment of protected areas such as National Parks, designed to preserve and expand the forests. (Full article...)
-
Image 4The Protected areas of New South Wales include both terrestrial and marine protected areas. there are 225 national parks in New South Wales. A number established since the late 1970s followed campaigns by local residents and environmentalists.
Based on the Collaborative Australian Protected Area Database (CAPAD) 2020 data there are 2136 separate terrestrial protected areas with a total land area of 7,696,641 hectares (19,018,810 acres) (9.61% of the state's area). CAPAD data also shows 18 marine protected areas with a total area of 348,849 hectares (862,020 acres), covering 39.63% of NSW waters. (Full article...) -
Image 5This is a list of protected areas of Afghanistan.
- Ab-i-Estada Nature Reserve, Ghazni Province
- Ajar Valley Nature Reserve, Bamyan Province
- Bamiyan National Heritage Park, Bamyan Province
- Bamiyan Plateau Protected Landscape, Bamyan Province
- Band-e Amir National Park, Bamyan Province
- Darqad (Takhar) Wildlife Reserve, Takhar Province
- Dasht-i-Nawar Waterfowl Sanctuary, Ghazni Province
- Hamun-i-Puzak Waterfowl Sanctuary, Farah and Nimroz provinces
- Imam Sahib (Kunduz) Wildlife Reserve, Kunduz Province
- Khulm Landmark Protected Area, Balkh Province
- Koh-e Baba (Shah Foladi) Protected Landscape, Bamyan province
- Kol-i-Hashmat Khan Waterfowl Sanctuary, Kabul Province
- Northwest Afghanistan Game Managed Reserve, Herat Province
- Nuristan National Park and Wildlife Reserve, Nuristan Province
- Pamir-i-Buzurg Wildlife Reserve, Badakhshan Province
- Registan Desert Wildlife Managed Reserve, Kandahar Province
- Wakhan National Park, Badakhshan Province
- Zadran National Reserve, Paktia Province
-
Image 6The protected areas of South Africa include national parks and marine protected areas managed by the national government, public nature reserves managed by provincial and local governments, and private nature reserves managed by private landowners. Most protected areas are intended for the conservation of flora and fauna. National parks are maintained by South African National Parks (SANParks). A number of national parks have been incorporated in transfrontier conservation areas.
Protected areas may also be protected for their value and importance as historical, cultural heritage or scientific sites. More information on these can be found in the list of heritage sites in South Africa. (Full article...) -
Image 7

A family of Asiatic lions at Gir National Park
The Gujarat state of western India has four National Parks and twenty-three wildlife sanctuaries which are managed by the Forest Department of the Government of Gujarat. (Full article...) -
Image 8A list of protected areas of Oman:
- Al Wusta Wildlife Reserve
- Ra's Al Hadd Turtle Reserve
- Ad Dimaniyat Islands Reserve
- Al Saleel National Park (As Salil Natural Park)
- Jabal Samhan Nature Reserve
- Al Jabal Al Akhdar Scenic Reserve
- Western Hajer Stars Lights Reserve
- Arabian Oryx Sanctuary
- Al Rustaq Wildlife Reserve
- Al Wusta Wetland Reserve
- Jabal Qahwan Nature Reserve
- Al Sareen Nature Reserve
- Ras al Shajar Nature Reserve
- Al Khuwuair Nature Reserve
- Khawrs of the Salalah Coast Reserve
-
Image 9Protected areas of Slovenia include one national park (Slovene: narodni park), three regional parks (regijski park), several natural parks (krajinski park), and hundreds of natural monuments (naravni spomenik) and monuments of designed nature (spomenik oblikovane narave). They cover about 12.5% of the Slovenian territory. Under the Wild Birds Directive, 26 sites totalling roughly 25% of the nation's land are "Special Protected Areas"; the Natura 2000 proposal would increase the totals to 260 sites and 32% of national territory. (Full article...)
-
Image 10

The protected areas of Bhutan are its national parks, nature preserves, and wildlife sanctuaries. Most of these protected areas were first set aside in the 1960s, originally covering most of the northern and southern regions of Bhutan. Today, protected areas cover more than 42% of the kingdom, mostly in the northern regions. Protected areas also line most of Bhutan's international borders with China and India. (Full article...) -
Image 11Papua New Guinea is home to several protected areas, which receive protection because of their environmental, cultural or similar value.
The total area of Papua New Guinea protected territories is 14,330 km2 (5,530 sq mi), which amounts to approximately 3.07% of the country's territory. The total number of protected areas as 2018 is 71. (Full article...) -
Image 12
Grand Canyon of Yellowstone
The protected areas of the United States are managed by an array of different federal, state, tribal and local level authorities and receive widely varying levels of protection. Some areas are managed as wilderness, while others are operated with acceptable commercial exploitation. , the 42,826 protected areas covered 1,235,486 km2 (477,024 sq mi), or 13 percent of the land area of the United States. This is also one-tenth of the protected land area of the world. The U.S. also had a total of 871 National Marine Protected Areas, covering an additional 1,240,000 sq mi (3,200,000 km2), or 26 percent of the total marine area of the United States. (Full article...) -
Image 13

Desert landscape in Qatar
Protected areas of Qatar include:- Al Reem Biosphere Preserve (designated in 2007) is part of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves in the Arab States
- Al Shahaniyah Park in Al-Shahaniya
- Al Thakira Nature Reserve in Al Thakhira
- Al Wabra Wildlife Preservation
- Dahl Al Hammam Park, a sinkhole in Doha (entrance to the hole is now closed to the public)
- Khor Al Adaid Natural Reserve in Khor Al Adaid
- Khor Al Udeid Fish Sanctuary
- Mudhlem Cave in Mukaynis
- Musfer Sinkhole in Salwa
- Ras Abrouq Nature Reserve (also known as Bir Zekreet (Zekreet Beach)) in Ras Abrouq
- Ras Ushairij Gazelle Conservation Park
- Umm Tais National Park
-
Image 14

Network of protected areas in Albania (2020)
Despite being a relatively small country, Albania is exceedingly rich in biodiversity. Its ecosystems and habitats support over 5,550 species of vascular and non-vascular plants and more than 15,600 species of coniferous and non-coniferous evergreens, most of which are threatened at global and European levels. The country has made recent efforts to expand its network of protected areas which now include: 11 national parks, 1 marine park, 718 nature monuments, 23 managed nature reserves, 11 protected landscapes, 4 World Heritage Sites, 4 Ramsar sites and other protected areas of various categories, that when combined, account for 21.36% of the territory. Furthermore, a biosphere reserve, 45 important plant areas and 16 important bird areas are found in the country.
Meanwhile, the central government has proclaimed the Coastline and the Tirana Greenbelt as areas of national importance. (Full article...) -
Image 15Cadw is the historic environment service of the Welsh Government which manages historical buildings and ancient monuments in Wales. (Full article...)
Selected world maps
-
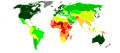
Image 1United Nations Human Development Index map by country (2016)
-
Image 2The world map by Gerardus Mercator (1569), the first map in the well-known Mercator projection
-
Image 3Only a few of the largest large igneous provinces appear (coloured dark purple) on this geological map, which depicts crustal geologic provinces as seen in seismic refraction data
-
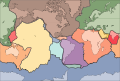
Image 4A plate tectonics map with volcano locations indicated with red circles
-
Image 51516 map of the world by Martin Waldseemüller
-
Image 6Mollweide projection of the world
-
Image 7Time zones of the world
-
Image 8The Goode homolosine projection is a pseudocylindrical, equal-area, composite map projection used for world maps.
-
Image 9Index map from the International Map of the World (1:1,000,000 scale)
World records
- List of Olympic records in athletics
- List of world records in athletics
- List of junior world records in athletics
- List of world records in masters athletics
- List of world youth bests in athletics
- List of IPC world records in athletics
- List of world records in canoeing
- List of world records in chess
- List of cycling records
- List of world records in track cycling
- List of world records in finswimming
- List of world records in juggling
- List of world records in rowing
- List of world records in speed skating
- List of world records in swimming
- List of IPC world records in swimming
- List of world records in Olympic weightlifting
Topics
Continents of Earth | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
| Cenozoic Era (present–66.0 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesozoic Era (66.0–252 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
| Paleozoic Era (252–539 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
| Proterozoic Eon (539 Ma–2.5 Ga) |
| ||||||||||||
| Archean Eon (2.5–4 Ga) | |||||||||||||
| Hadean Eon (4–4.6 Ga) | |||||||||||||
ka = kiloannum (thousands years ago); Ma = megaannum (millions years ago); Ga = gigaannum (billions years ago). See also: Geologic time scale • | |||||||||||||
| City proper | |
|---|---|
| Metropolitan area | |
| Urban area/agglomeration | |
| Historical | |
| Related articles | |
| Locations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Related | ||
| Retrospectively recognized expositions | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIE-recognized Universal expositions | |||||||||||||
| BIE-recognized specialized expositions |
| ||||||||||||
| BIE-recognized horticultural exhibitions (AIPH) | |||||||||||||
| Not BIE- recognized |
| ||||||||||||
†Postponed to 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic | |||||||||||||
| Confederations | |
|---|---|
| World Championships | |
| World Cup | |
| Special events | |
| Presidents |
|
| Awards | |
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
Economic classification of countries | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Three-World Model | |||||
| Gross domestic product (GDP) |
| ||||
| Gross national income (GNI) | |||||
| Wages | |||||
| Wealth | |||||
| Other national accounts | |||||
| Human development | |||||
| Digital divide | |||||
| Net international investment position (NIIP) | |||||
| Technological |
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sociological | |||||
| Ecological |
| ||||
| Biological |
| ||||
| Astronomical | |||||
| Eschatological |
| ||||
| Others |
| ||||
| Fictional | |||||
| Organizations | |||||
| Theatres |
| ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Principal participants |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Timeline |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Aspects |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| General |
| ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participants |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Timeline |
| ||||||||||||||||
Categories
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus