1,3-Indandione
Today we are going to delve into the fascinating world of 1,3-Indandione. Since time immemorial, 1,3-Indandione has captured the attention and interest of millions of people around the world. Whether due to its impact on society, its influence on popular culture or its relevance in history, 1,3-Indandione has left an indelible mark on humanity. In this article, we will delve into the many facets of 1,3-Indandione, exploring its meaning, its evolution over time, and its importance in the current context. Join us on this journey to discover everything 1,3-Indandione has to offer and how it has shaped our world in ways we may have never imagined before.

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1H-Indene-1,3(2H)-dione | |
| Other names
Indandione; 1,3-Diketohydrindene; 1,3-Dioxoindane; 1,3-Hydrindendione
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.191 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H6O2 | |
| Molar mass | 146.145 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 1.37 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 129 to 132 °C (264 to 270 °F; 402 to 405 K) |
| slight | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
1,3-Indandione (sometimes simply indanedione) is an organic compound with the molecular formula C6H4(CO)2CH2. It is a β-diketone with indane as its structural nucleus. It is a colorless or white solid, but old samples can appear yellowish or even green. It is a popular chemical scaffold (building block of various useful chemical compounds).
Structural properties
Solid 1,3-indandione is a diketone, As a solution in water, it is partially (~2%) enolized. The enolate anion exhibits significant delocalization, and the highest electron density is on the second carbon. This acid-base behavior explains many properties of the compound.[citation needed]
Preparation
1,3-Indandione can be prepared by decarboxylation of the sodium salt of 2-ethoxycarbonyl-1,3-indandione, which itself is obtained by Claisen condensation of ethyl acetate and dimethyl phthalate.[citation needed]
Chemical properties
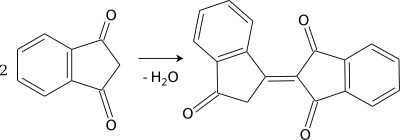
The carbon at the C-2 position is alpha to both carbonyls, and thus can act as a nucleophile. It undergoes self-aldol condensation quite easily, resulting in bindone.
Bromination occurs at the 2-position:
One or both carbonyl groups can be reduced to alcohol groups or methylene groups, depending on the method used.
See also
References
- ^ 1,3-Indandione at Sigma-Aldrich
- ^ MSDS at Acros Organics, retrieved on June 16, 2011
- ^ (in Russian) Нейланд О. Я. Органическая химия: Учеб. для хим. спец. вузов. Москва: Высшая школа, 1990.— с. 481—490.
- ^ Dumur, Frédéric (2021). "Recent advances on visible light photoinitiators of polymerization based on Indane-1,3-dione and related derivatives". European Polymer Journal. 143: 110178. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2020.110178. S2CID 229445473.
- ^ Pluskota, Robert; Koba, Marcin (2018). "Indandione and Its Derivatives - Chemical Compounds with High Biological Potential". Mini-Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry. 18 (15): 1321–1330. doi:10.2174/1389557518666180330101809. PMID 29600759. S2CID 4516564.
External links
 Media related to 1,3-Indandione at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to 1,3-Indandione at Wikimedia Commons