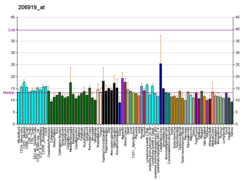
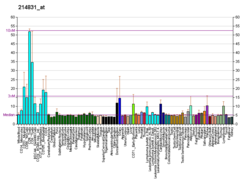
ELK4
In today's world, ELK4 has gained unprecedented relevance. With the advancement of technology and globalization, ELK4 has become a topic of interest and discussion everywhere. From its origins to its influence today, ELK4 has played a fundamental role in people's lives and in the development of society. Over the years, numerous studies and research have been carried out in order to better understand the impact of ELK4 and its implications in different areas. Therefore, it is essential to carefully analyze ELK4 and its various dimensions, in order to have a more complete and precise vision on this topic.
ETS domain-containing protein Elk-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ELK4 gene.[5][6][7]
Function
This gene is a member of the Ets family of transcription factors and of the ternary complex factor (TCF) subfamily. Proteins of the TCF subfamily form a ternary complex by binding to the serum response factor and the serum response element in the promoter of the c-fos proto-oncogene. The protein encoded by this gene is phosphorylated by the kinases, MAPK1 and MAPK8. Several transcript variants have been described for this gene.[7]
Interactions
ELK4 has been shown to interact with:
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000158711 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000026436 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Shipley J, Sheer D, Dalton S, Treisman R, Patel K (Mar 1995). "Mapping of the human SAP1 (SRF accessory protein 1) gene and SAP2, a gene encoding a related protein, to chromosomal bands 1q32 and 12q23, respectively". Genomics. 23 (3): 710–1. doi:10.1006/geno.1994.1564. PMID 7851904.
- ^ Giovane A, Sobieszczuk P, Mignon C, Mattei MG, Wasylyk B (Mar 1996). "Locations of the ets subfamily members net, elk1, and sap1 (ELK3, ELK1, and ELK4) on three homologous regions of the mouse and human genomes". Genomics. 29 (3): 769–72. doi:10.1006/geno.1995.9938. PMID 8575773.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: ELK4 ELK4, ETS-domain protein (SRF accessory protein 1)".
- ^ Chai Y, Chipitsyna G, Cui J, Liao B, Liu S, Aysola K, Yezdani M, Reddy ES, Rao VN (Mar 2001). "c-Fos oncogene regulator Elk-1 interacts with BRCA1 splice variants BRCA1a/1b and enhances BRCA1a/1b-mediated growth suppression in breast cancer cells". Oncogene. 20 (11): 1357–67. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1204256. PMID 11313879.
- ^ Hassler M, Richmond TJ (Jun 2001). "The B-box dominates SAP-1-SRF interactions in the structure of the ternary complex". EMBO J. 20 (12): 3018–28. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.12.3018. PMC 150215. PMID 11406578.
- ^ Zhu C, Johansen FE, Prywes R (Sep 1997). "Interaction of ATF6 and serum response factor". Mol. Cell. Biol. 17 (9): 4957–66. doi:10.1128/MCB.17.9.4957. PMC 232347. PMID 9271374.
Further reading
- Sharrocks AD, Brown AL, Ling Y, Yates PR (1998). "The ETS-domain transcription factor family". Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 29 (12): 1371–87. doi:10.1016/S1357-2725(97)00086-1. PMID 9570133.
- Wasylyk B, Hagman J, Gutierrez-Hartmann A (1998). "Ets transcription factors: nuclear effectors of the Ras-MAP-kinase signaling pathway". Trends Biochem. Sci. 23 (6): 213–6. doi:10.1016/S0968-0004(98)01211-0. PMID 9644975.
- Dalton S, Treisman R (1992). "Characterization of SAP-1, a protein recruited by serum response factor to the c-fos serum response element". Cell. 68 (3): 597–612. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(92)90194-H. PMID 1339307. S2CID 26274460.
- Price MA, Rogers AE, Treisman R (1995). "Comparative analysis of the ternary complex factors Elk-1, SAP-1a and SAP-2 (ERP/NET)". EMBO J. 14 (11): 2589–601. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07257.x. PMC 398373. PMID 7540136.
- Adams MD, Kerlavage AR, Fleischmann RD, Fuldner RA, Bult CJ, Lee NH, Kirkness EF, Weinstock KG, Gocayne JD, White O (1995). "Initial assessment of human gene diversity and expression patterns based upon 83 million nucleotides of cDNA sequence" (PDF). Nature. 377 (6547 Suppl): 3–174. PMID 7566098.
- Dalton S, Treisman R (1994). "Characterization of SAP-1, a protein recruited by serum response factor to the c-fos serum response element" (PDF). Cell. 76 (2): 411. PMID 8293474. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-09-28. Retrieved 2011-06-29.
- Janknecht R, Hunter T (1997). "Activation of the Sap-1a transcription factor by the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) mitogen-activated protein kinase". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (7): 4219–24. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.7.4219. PMID 9020136.
- Janknecht R, Hunter T (1997). "Convergence of MAP kinase pathways on the ternary complex factor Sap-1a". EMBO J. 16 (7): 1620–7. doi:10.1093/emboj/16.7.1620. PMC 1169766. PMID 9130707.
- Stein B, Yang MX, Young DB, Janknecht R, Hunter T, Murray BW, Barbosa MS (1997). "p38-2, a novel mitogen-activated protein kinase with distinct properties". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (31): 19509–17. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.31.19509. PMID 9235954.
- Mo Y, Vaessen B, Johnston K, Marmorstein R (1998). "Structures of SAP-1 bound to DNA targets from the E74 and c-fos promoters: insights into DNA sequence discrimination by Ets proteins". Mol. Cell. 2 (2): 201–12. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80130-6. PMID 9734357.
- Yates PR, Atherton GT, Deed RW, Norton JD, Sharrocks AD (1999). "Id helix-loop-helix proteins inhibit nucleoprotein complex formation by the TCF ETS-domain transcription factors". EMBO J. 18 (4): 968–76. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.4.968. PMC 1171189. PMID 10022839.
- Kamakura S, Moriguchi T, Nishida E (1999). "Activation of the protein kinase ERK5/BMK1 by receptor tyrosine kinases. Identification and characterization of a signaling pathway to the nucleus". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (37): 26563–71. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.37.26563. PMID 10473620.
- Chai Y, Chipitsyna G, Cui J, Liao B, Liu S, Aysola K, Yezdani M, Reddy ES, Rao VN (2001). "c-Fos oncogene regulator Elk-1 interacts with BRCA1 splice variants BRCA1a/1b and enhances BRCA1a/1b-mediated growth suppression in breast cancer cells". Oncogene. 20 (11): 1357–67. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1204256. PMID 11313879.
- Hassler M, Richmond TJ (2001). "The B-box dominates SAP-1-SRF interactions in the structure of the ternary complex". EMBO J. 20 (12): 3018–28. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.12.3018. PMC 150215. PMID 11406578.
- Mo Y, Ho W, Johnston K, Marmorstein R (2002). "Crystal structure of a ternary SAP-1/SRF/c-fos SRE DNA complex". J. Mol. Biol. 314 (3): 495–506. doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.5138. PMID 11846562.
External links
- ELK4+protein,+human at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- FactorBook ELK4
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.