Kadamba script
Nowadays, Kadamba script has become a very important issue in modern society. With the advancement of technology and constant changes in the world, Kadamba script has become relevant in various areas of daily life. From politics to popular culture, economics and education, Kadamba script has significantly impacted the way we interact with the world around us. In this article, we will explore in depth the importance of Kadamba script and its influence on our daily lives, analyzing the various facets that surround it and its impact on today's society.
| Kadamba script | |
|---|---|
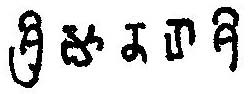 | |
| Script type | |
Period | 4–7th century CE[1] |
| Direction | Left-to-right |
| Languages | Old Kannada Old Telugu Sanskrit Konkani |
| Related scripts | |
Parent systems | |
Child systems | Kannada-Telugu alphabet, Goykanadi,[2] Pyu script[3] |
| Brahmic scripts |
|---|
| The Brahmi script and its descendants |
The Kadamba script is the first writing system devised specifically for writing Kannada, and later adopted to write Telugu language.[4] The Kadamba script is also known as Pre-Old-Kannada script.
The Kadamba script is one of the oldest scripts of the southern group of writing systems that developed from the ancient Brahmi script. By the 5th century CE it became distinct from other Brahmi variants and was used in what are now the South Indian states of Karnataka, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh. It evolved into the Kannada-Telugu script by the 10th century CE and was used to write the Kannada and Telugu languages.[5] It is also distantly related to the Sinhala script.[6]
History
During the rule of Kadamba dynasty (325-550), major change in the Brahmi script resulted in the Kadamba Kannada script, letters were shorter and round in shape. During (325 to 1000 AD) the rule of the Western Ganga dynasty in the southern parts of Karnataka the Kannada script used differently (also known as Ganga script) in rock edicts and copper plate inscriptions. During 6th to 10th century, the Telugu-Kannada alphabet stabilized during the rule of the Chalukyas of Badami from 500-1000[7] and Rastrakutas.[citation needed]
Inscriptions in Kadamba script


- Gudnapur Inscription on 20-foot-long stone pillar written in Kadamba script[8]
- Copper plate inscriptions in Kadamba (Pre - Chalukya) script, Kadamba-Pallava script, Kannada-Telugu script are available at Chennai museum[9]
- Halmidi inscription
- Talagunda pillar inscription[10]
Similarity with other scripts
The Kadamba script shares similarities with scripts of certain languages belonging to the alphasyllabary or abugida family, including Goykanadi, Bhattiprolu script, Salankayana script,[11] Pallava script, Gupta script,[12] as well as the Tulu script.[13]

See also
References
- ^ Diringer, David (1948). Alphabet a key to the history of mankind. p. 381.
- ^ "Goykanadi script".
- ^ Aung-Thwin, Michael (2005). The mists of Rāmañña: The Legend that was Lower Burma (illustrated ed.). Honolulu: University of Hawai'i Press. ISBN 978-0-8248-2886-8.
- ^ Diringer, David (1948). Alphabet a key to the history of mankind. p. 381.
- ^ "Scripts fading away with time". Retrieved 28 August 2013.
- ^ Jayarajan, Paul M. (1 January 1976). History of the Evolution of the Sinhala Alphabet. Colombo Apothecaries' Company, Limited.
- ^ Kipfer, Barbara Ann (2000). Encyclopedic Dictionary of Archaeology. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 692. ISBN 978-0-306-46158-3.
- ^ Rajiv Ajjibal (16 December 2011). "Monuments crying for attention". The Hindu. Retrieved 13 March 2014.
- ^ "Government Museum Chennai". Chennaimuseum.org. Retrieved 13 March 2014.
- ^ "Kannada inscription at Talagunda may replace Halmidi as oldest". Deccan Herald. 12 January 2017.
- ^ "Comparison of Brahmi and Pallava scripts". SkyKnowledge.com. Retrieved 14 December 2025.
- ^ "Gupta". Ancient Scripts. Archived from the original on 7 March 2020. Retrieved 13 March 2014.
- ^ "Comparison of scripts (Tulu/Kadamba)". Quora. Archived from the original on 17 October 2013. Retrieved 28 June 2014.




