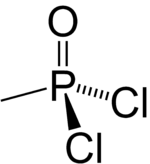
Methylphosphonyl dichloride
In this article we are going to delve into the fascinating world of Methylphosphonyl dichloride. Whether you are interested in learning more about Methylphosphonyl dichloride, or are simply looking for up-to-date information on the topic, this article aims to provide you with all the information you need. We will explore the most important aspects related to Methylphosphonyl dichloride, from its origin and history to its relevance today. Regardless of whether you are an expert on the subject or simply curious, we are sure that you will find this article interesting and enriching.
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methylphosphonic dichloride | |
| Other names
Methanephosphonic dichloride
Methanephosphonic acid dichloride Methylphosphonyl dichloride Dichloro | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.578 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UN number | 9206 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CH3Cl2OP | |
| Molar mass | 132.91 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Density | 1.468 g/mL at 20 °C |
| Melting point | 28 to 34 °C (82 to 93 °F; 301 to 307 K) |
| Boiling point | 163 °C (325 °F; 436 K) |
| Reacts with water | |
| Solubility | Ether, THF |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Very toxic, reacts with water |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H314, H330 | |
| P260, P264, P271, P280, P284, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P320, P321, P363, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | >110 °C |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
26 ppm/4h by inhalation (rat) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Methylphosphonyl dichloride (DC) or dichloro is an organophosphorus compound. It has a number of commercial uses[vague] but is most notable as being a precursor to several chemical weapons agents. It is a white crystalline solid that melts slightly above room temperature.
Synthesis and reactions
Methylphosphonyl dichloride is produced by oxidation of methyldichlorophosphine, with sulfuryl chloride:
- CH3PCl2 + SO2Cl2 → CH3P(O)Cl2 + SOCl2
It can also be produced from a range of methylphosphonates (e.g. dimethyl methylphosphonate) via chlorination with thionyl chloride. Various amines catalyse this process. With hydrogen fluoride or sodium fluoride, it can be used to produce methylphosphonyl difluoride. With alcohols, it converts to the dialkoxide:
- CH3P(O)Cl2 + 2 HOR → CH3P(O)(OR)2 + HCl
Safety
Methylphosphonyl dichloride is very toxic and reacts vigorously with water to release hydrochloric acid. It is also listed under Schedule 2 of the Chemical Weapons Convention as it is used in the production of organophosphorus nerve agents such as sarin and soman.
References
- ^ "SAFETY DATA SHEET Methylphosphonic dichloride". SAFETY DATA SHEET Methylphosphonic dichloride. MilliporeSigma. June 26, 2020. Retrieved April 27, 2022.
- ^ Svara, J.; Weferling, N.; Hofmann, T. "Phosphorus Compounds, Organic," In 'Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2008. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_545.pub2.
- ^ Maier, Ludwig (1990). "Organic Phosphorus Compounds 90.l A Convenient, One-Step Synthesis of Alkyl- and Arylphosphonyl Dichlorides". Phosphorus, Sulfur, and Silicon and the Related Elements. 47 (3–4): 465–470. doi:10.1080/10426509008038002.
- ^ Carl Patois, Philippe Savignac, Elie About-Jaudet, Noël Collignon (1996). "Bis(Trifluoroethyl) (carboethoxymethyl)phosphonate". Organic Syntheses. 73: 152. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.073.0152.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)